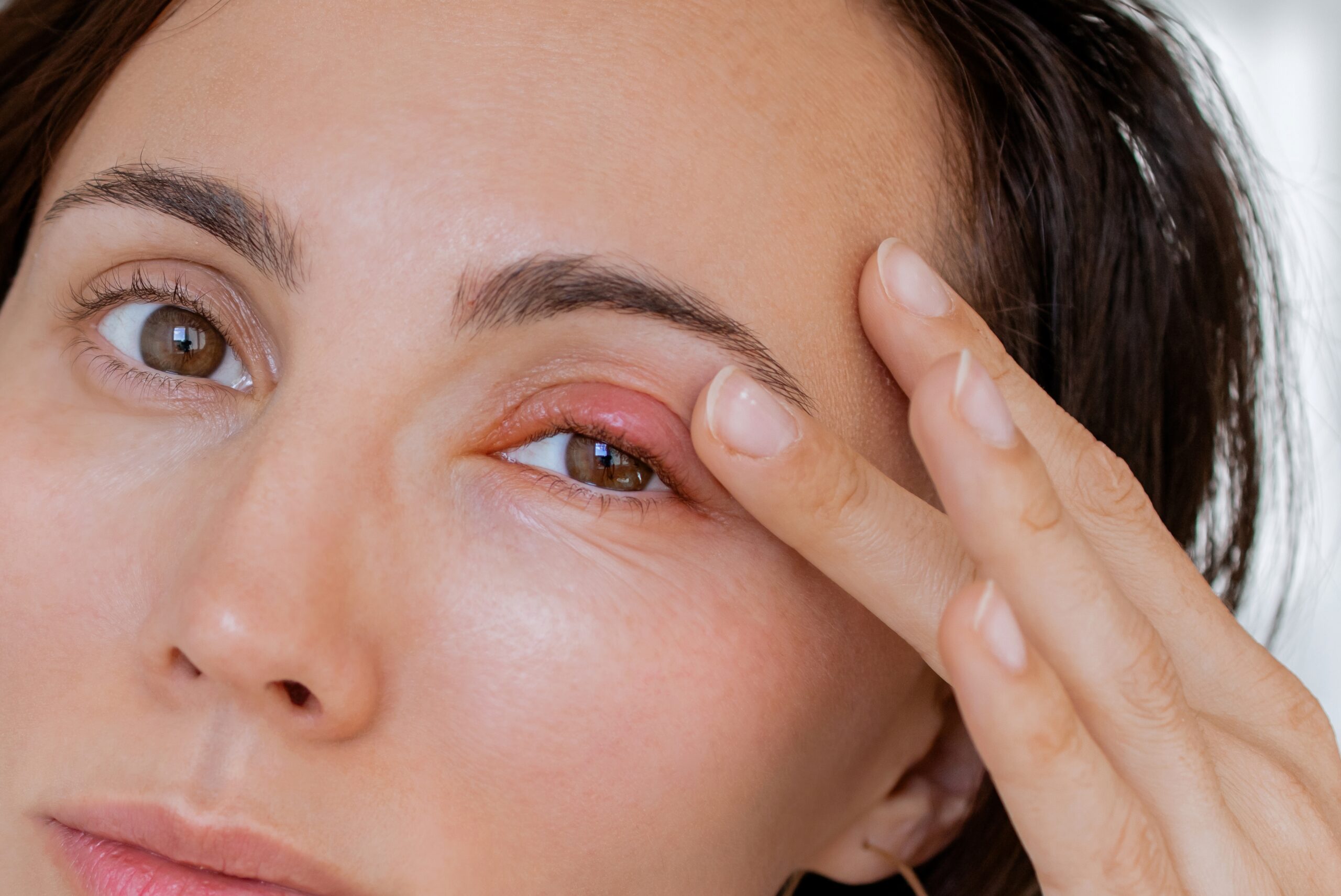
Have you discovered a painful, red bump on your eyelid? It could be a stye.
Styes can cause a gritty feeling in your eye and make blinking uncomfortable. While many styes go away on their own, others are stubborn and require treatment.
Keep reading to learn more about what a stye is, when you should be concerned, and when to seek treatment!
What is a Stye?
A stye or hordeolum is a painful, red bump on the edge of your eyelid that has become infected by bacteria, usually Staphylococcus aureus. It may look like a pimple or boil.
A stye often develops on one eyelid. But it’s also possible to have styes on both eyelids.
What are the Different Types of Styes?
There are two types of styes:
External Stye: An external stye is the most common type. It develops on the outer edge of the lower or upper eyelid, close to the lashes.
Internal Stye: An internal stye forms on the inside of the upper or lower eyelids.
What are the Symptoms of a Stye?
The symptoms of a stye may include:
- Tearing
- Eye discharge
- Swelling of the eyelid
- Light sensitivity
- Red, painful lump
- Itching and soreness
- Crusting along the lids
- A feeling that something is in the eye
What are the Causes and Risk Factors of a Stye?
A stye occurs when a tiny oil gland close to your lashes gets blocked and infected, often by bacteria. You’re also more likely to get styes due to certain risk factors.
- Diabetes
- High cholesterol
- Hormonal changes
- You’ve previously had a stye
- Blepharitis
- Rosacea
- Habits that increase the chances of infection, such as using old cosmetics, touching or rubbing your eyes with unwashed hands, sleeping with eye makeup, or poor contact lens hygiene
When Should You Be Concerned About a Stye?
Styes typically last for a week or two and often clear up on their own without treatment. You can relieve the discomfort or pain of a stye by applying a warm washcloth to the eyelid for fifteen minutes at a time, three to four times daily.
Infections that don’t completely heal may lead to more severe infections that can spread to other areas or affect your vision. You should be concerned and visit your eye doctor if your stye hasn’t resolved within one to two weeks or is accompanied by the following symptoms:
- Recurring styes
- Chills or a fever
- A very large or painful stye
- An eyelid that’s swollen shut
- Thick blood or discharge oozing from the stye
- Swelling and redness that extends into the cheek or other parts of the face
- Vision changes, including double or blurred vision
While your eye will likely be watery and red, your vision should still be clear. If you notice vision changes, be sure to visit your eye doctor right away.
What are the Treatment Options for Styes?
Your eye doctor may recommend treatments such as:
Antibiotics
Your eye doctor can prescribe a topical antibiotic cream or antibiotic eye drops to help fight the infection. If the area around your eye is infected, too, your eye doctor may prescribe antibiotics to take by mouth.
Removal Procedure
Minor surgery might be required in some cases. During the procedure, your eye doctor will numb the area and make a small cut in the stye to lance and express the stye.
Say Goodbye to Styes
If you suspect you have a stye, you can find relief at VisionPoint Eye Center. Our experienced eye doctors will diagnose and treat your stye so you can feel better quickly and get back to enjoying everyday activities.
Have you noticed an odd bump on your eyelid? Schedule your appointment at VisionPoint Eye Center in Bloomington, IL, today to receive an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan from one of our knowledgeable eye doctors.